How Payment Processing Works: Unlocking the Secrets to Secure and Efficient Transactions
Learn how payment processing works and optimize your business transactions for security and efficiency. Boost your business now!
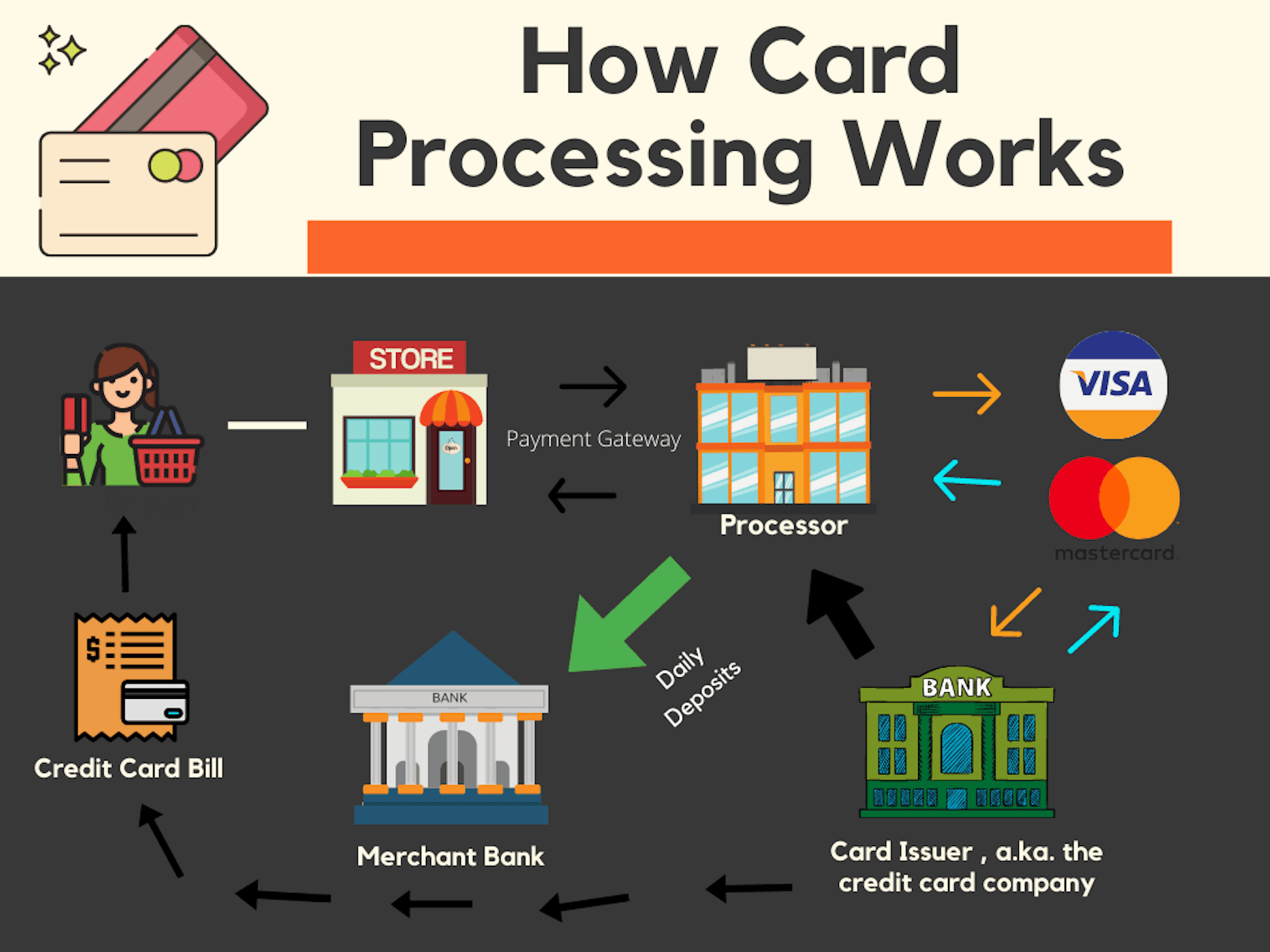
Payment processing is a crucial aspect of modern commerce, enabling businesses to accept payments from customers efficiently and securely. This article provides a comprehensive overview of how payment processing works, including its mechanisms, benefits, and how businesses can implement and optimize their payment systems.
Key Takeaways
Payment processing involves multiple parties and steps to securely transfer funds from customers to merchants.
The main steps in payment processing are authorization, authentication, and settlement.
Payment gateways and processors play crucial roles in facilitating transactions.
Understanding Payment Processing
Payment processing refers to the series of actions that occur when a customer makes a payment to a business. This process involves multiple parties, including the customer, the merchant, payment processors, banks, and payment networks. The main goal is to securely transfer funds from the customer's account to the merchant's account.
Key Entities in Payment Processing
Merchant: The business that sells goods or services and accepts payments.
Customer: The individual making the purchase.
Payment Gateway: A technology that captures and transfers payment data from the customer to the merchant's bank.
Payment Processor: A company that handles the transaction process, including authorization, authentication, and settlement.
Issuing Bank: The bank that issued the customer's credit or debit card.
Acquiring Bank: The bank that processes payments on behalf of the merchant.
Payment Network: Companies like Visa, MasterCard, and American Express that facilitate communication between the issuing and acquiring banks.
Steps in Payment Processing
The payment processing journey can be broken down into three main steps:
1. Authorization
When a customer makes a purchase, they present their card information (either physically or digitally).
The payment gateway captures this information and sends it to the payment processor.
The payment processor forwards the transaction details to the issuing bank to check if the customer has sufficient funds.
The issuing bank either approves or declines the transaction based on the customer's account status.
2. Authentication
If the transaction is approved, the payment processor verifies the authenticity of the card and the transaction.
This may involve additional security measures, such as 3D Secure, which requires the customer to enter a password or code.
3. Settlement
Once the transaction is authenticated, the payment processor initiates the transfer of funds from the customer's account to the merchant's account.
The acquiring bank receives the funds and deposits them into the merchant's account, completing the transaction.
Importance of Payment Processing
Understanding payment processing is essential for businesses that want to accept online payments. It ensures smooth and secure transactions while protecting customer financial information. Additionally, businesses must choose a payment processor that aligns with their needs, as different processors offer various features, fees, and services.
Benefits of Efficient Payment Processing
Enhanced Security: Protects sensitive customer data through encryption and other security measures.
Faster Transactions: Reduces the time taken to complete transactions, improving customer satisfaction.
Reduced Fraud: Implements fraud detection mechanisms to prevent unauthorized transactions.
Global Reach: Enables businesses to accept payments from customers worldwide.
How to Choose a Payment Processor
Selecting the right payment processor is crucial for optimizing your payment system. Here are some factors to consider:
1. Transaction Fees
Different payment processors have varying fee structures, including flat fees, percentage-based fees, or a combination of both. Evaluate the costs and choose a processor that fits your budget.
2. Security Features
Ensure the payment processor offers robust security features, such as encryption, tokenization, and fraud detection, to protect customer data.
3. Integration Capabilities
Choose a payment processor that can easily integrate with your existing systems, such as e-commerce platforms, accounting software, and customer relationship management (CRM) systems.
4. Customer Support
Reliable customer support is essential for resolving any issues that may arise during transactions. Look for a processor that offers 24/7 support.
5. Global Acceptance
If you operate internationally, select a payment processor that supports multiple currencies and payment methods.
Optimizing Payment Processing
To ensure efficient and secure payment processing, businesses should implement best practices and stay updated with the latest technologies.
Best Practices for Payment Processing
Use Secure Payment Gateways: Choose reputable payment gateways that offer advanced security features.
Implement Fraud Detection Tools: Utilize tools that can identify and prevent fraudulent transactions.
Regularly Update Software: Keep your payment processing software up to date to protect against vulnerabilities.
Train Staff: Educate your team on best practices for handling payment data and recognizing potential security threats.
Leveraging APIs for Payment Processing
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) play a significant role in modern payment processing by enabling seamless integration between different systems. For more information on mastering API payment processing, refer to our detailed guide on Mastering API Payment Processing: The Ultimate Guide for Modern Businesses.
FAQs about Payment Processing
What is payment processing?
Payment processing is the sequence of actions that securely transfer funds between a payer (customer) and a payee (merchant).
What are the main steps in payment processing?
The main steps are authorization, authentication, and settlement.
What roles do payment gateways and processors play?
Payment gateways capture and transfer payment data, while payment processors handle the logistics of transactions.
Why is understanding payment processing important for businesses?
It helps ensure smooth and secure transactions and protects customer financial information.
What are the different types of payment processors available?
Various types of payment processors cater to different business needs, including traditional banks, independent sales organizations (ISOs), and payment service providers (PSPs).
How do fees vary among different payment processors?
Fees can vary based on the processor's pricing model, including flat fees, percentage-based fees, or a combination. It’s essential to compare pricing structures to find the best fit for your business.
What security measures are in place to protect customer data during transactions?
Security measures include encryption, tokenization, fraud detection tools, and compliance with industry standards like PCI-DSS.
Related Articles
Understanding Merchant Services: An Overview of Payment Processing and Its Crucial Role
Unlock the Power of API Payment Processing: A Comprehensive Guide for 2024
The Ultimate Guide to Mastering API Payment Processing: Boost Security and Efficiency
By understanding how payment processing works, businesses can make informed decisions about the systems they use to accept payments, ensuring a smooth and secure experience for their customers.
© 2025 Edge Payment Technologies, Inc.